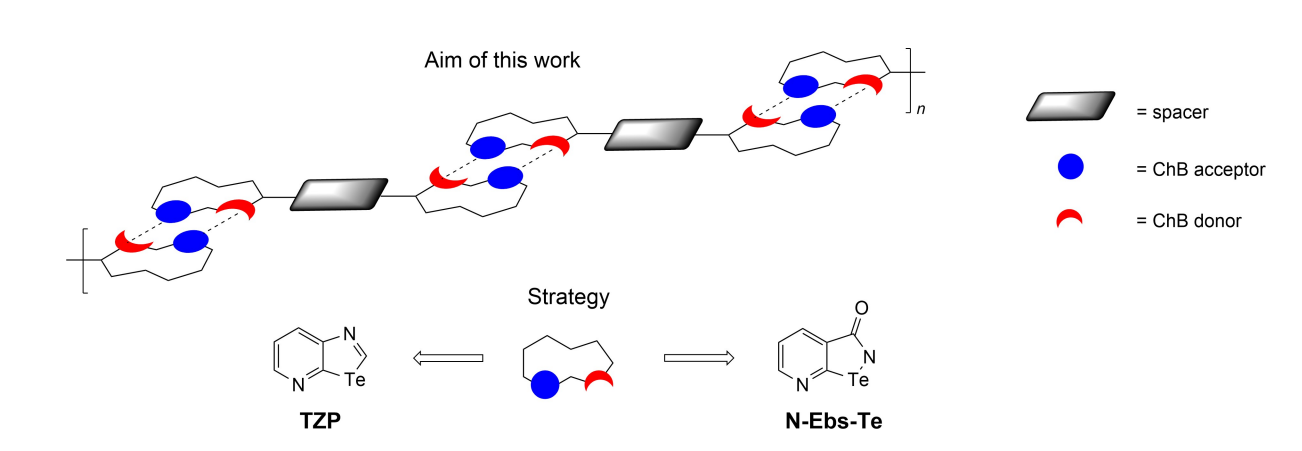
Aiming at the preparation of one-dimensional (1D) chalcogen-bonded supramolecular polymers at the solid state, this work describes the different syntheses which have been challenged to obtain ditopic molecular modules. At first, tellurazolopyridyl (TZP) rings have been chosen as recognition units, given their well-proven ability and persistency to self-assemble through double Te⋅⋅⋅N chalcogen bonds (ChBs). The second synthetic strategy dealt with the preparation of pyridyl-modified ebselen Te-containing analogues. By attempting several synthetic protocols, the targeted ebselen derivatives could not be obtained, whereas an unexpected Te-containing lactone as well as a spiro-type Te(IV)-containing derivatives were isolated, with the latter investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis.
Publications
Engineering Te-Containing Recognition Modules for ChalcogenBonding: Towards Supramolecular Polymeric Materials
peri-Acenoacene Ribbons with Zigzag BN-Doped Peripheries
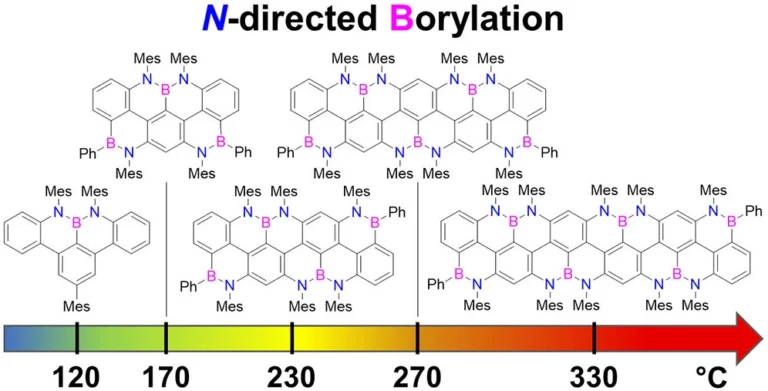
Here, we report the synthesis of BN-doped graphenoid nanoribbons, in which peripheral carbon atoms at the zigzag edges have been selectively replaced by boron and nitrogen atoms as BN and NBN motifs. This includes high-yielding ring closure key steps that, through N-directed borylation reaction using solely BBr3, allow the planarization of meta-oligoarylenyl precursors, through the formation of B–N and B–C bonds, to give ter-, quater-, quinque-, and sexi-arylenyl nanoribbons. X-ray single-crystal diffraction studies confirmed the formation of the BN and NBN motifs and the zigzag-edged topology of the regularly doped ribbons. Steady-state absorption and emission investigations at room temperature showed a systematic bathochromic shift of the UV–vis absorption and emission envelopes upon elongation of the oligoarylenyl backbone, with the nanoribbon emission featuring a TADF component. All derivatives displayed phosphorescence at 77 K. Electrochemical studies showed that the π-extension of the peri-acenoacene framework provokes a lowering of the first oxidative event (from 0.83 to 0.40 V), making these nanoribbons optimal candidates to engineer p-type organic semiconductors.
Tweaking the Optoelectronic Properties of S-Doped Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Chemical Oxidation
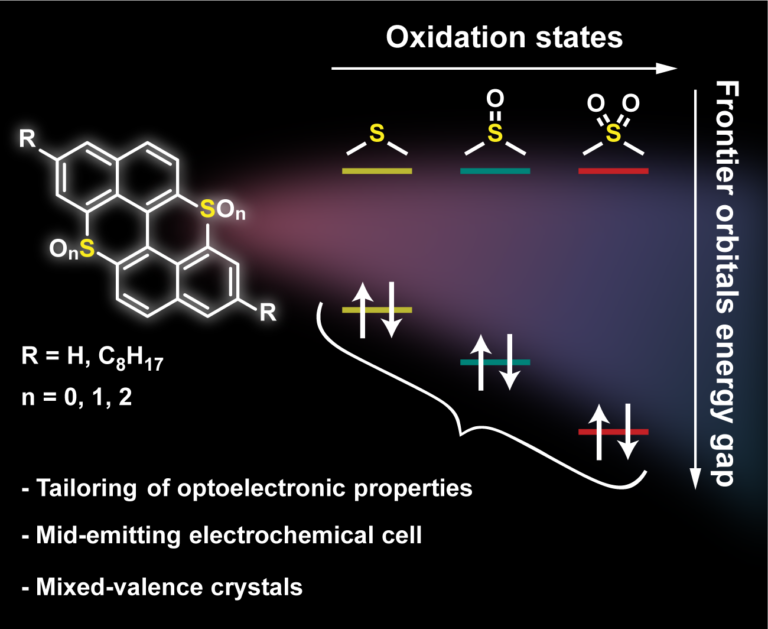
Peri-thiaxanthenothiaxanthene, an S-doped analog of peri-xanthenoxanthene, is used as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) scaffold to tune the molecular semiconductor properties by editing the oxidation state of the S-atoms. Chemical oxidation of peri-thiaxanthenothiaxanthene with H2O2 led to the relevant sulfoxide and sulfone congeners, whereas electrooxidation gave access to sulfonium-type derivatives forming crystalline mixed valence (MV) complexes. These complexes depicted peculiar molecular and solid-state arrangements with face-to-face p-p stacking organization. Photophysical studies showed a widening of the optical bandgap upon progressive oxidation of the S-atoms, with the bis-sulfone derivative displaying the largest value (E00 = 2.99 eV). While peri-thiaxanthenothiaxanthene showed reversible oxidation properties, the sulfoxide and sulfone derivatives mainly showed reductive events, corroborating their n-type properties. Electric measurements of single crystals of the MV complexes exhibited a semiconducting behavior with a remarkably high conductivity at room temperature (10-1-10-2 S cm-1 and 10-2-10-3 S cm-1 for the O and S derivatives, respectively), one of the highest reported so far. Finally, the electroluminescence properties of the complexes were tested in light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs), obtaining the first mid-emitting PAH-based LECs.
IGDQ motogenic peptide gradient induces directional cell migration through integrin (αv)β3 activation in MDA-MB-231 metastatic breast cancer cells
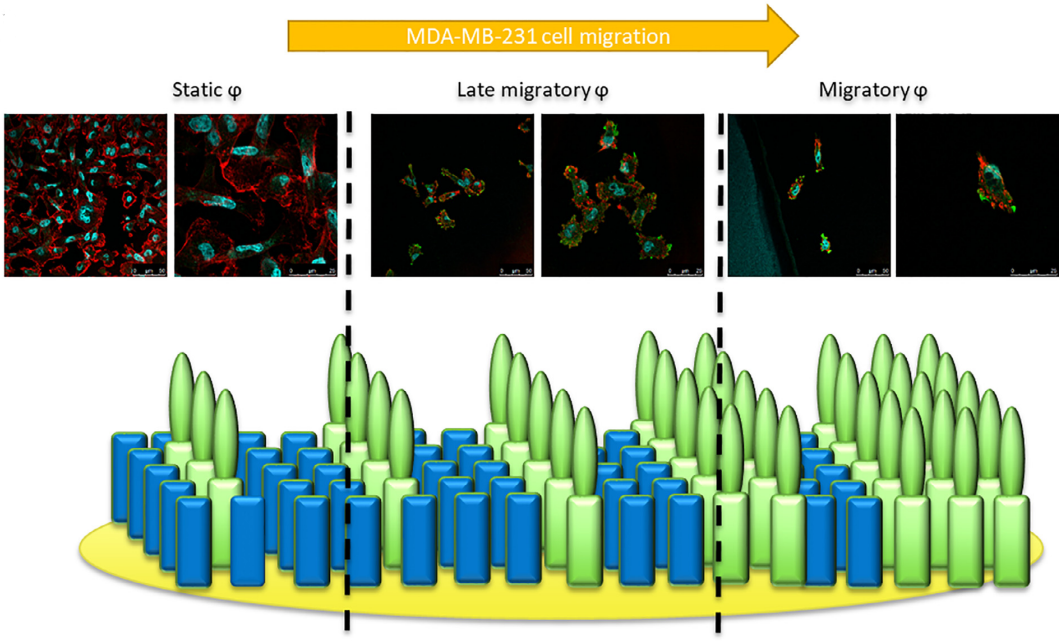
In the context of breast cancer metastasis study, we have shown in an in vitro model of cell migration that IGDQ-exposing (IsoLeu-Gly-Asp-Glutamine type I Fibronectin motif) monolayers (SAMs) on gold sustain the adhesion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by triggering Focal Adhesion Kinase and integrin activation. Such tunable scaffolds are used to mimic the tumor extracellular environment, inducing and controlling cell migration. The observed migratory behavior induced by the IGDQ-bearing peptide gradient along the surface allows to separate cell subpopulations with a “stationary” or “migratory” phenotype. In this work, we knocked down the integrins α5(β1) and (αv)β since they are already known to be implicated in cell migration. To this aim, a whole proteomic analysis was performed in beta 3 integrin (ITGB3) or alpha 5 integrin (ITGA5) knock-down MDA-MB-231 cells, in order to highlight the pathways implied in the integrin-dependent cell migration.
Our results showed that i) ITGB3 depletion influenced ITGA5 mRNA expression, ii) ITGB3 and ITGA5 were both necessary for IGDQ-mediated directional single cell migration and iii) integrin (αv)β3 was activated by IGDQ fibronectin type I motif. Finally, the proteomic analysis suggested that co-regulation of recycling transport of ITGB3 by ITGA5 is potentially necessary for directional IGDQ-mediated cell migration.
Boron Nitride-Doped Polyphenylenic Organogels
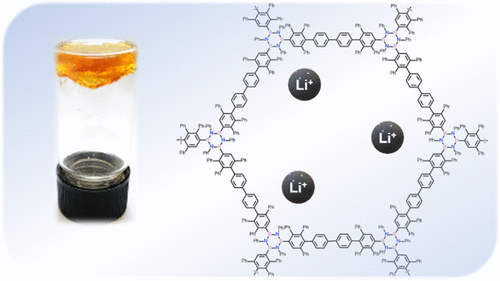
Herein, we describe the synthesis of the first boron nitride-doped polyphenylenic material obtained through a [4 + 2] cycloaddition reaction between a triethynyl borazine unit and a biscyclopentadienone derivative, which undergoes organogel formation in chlorinated solvents (the critical jellification concentration is 4% w/w in CHCl3). The polymer has been characterized extensively by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, solid-state 13C NMR, solid-state 11B NMR, and by comparison with the isolated monomeric unit. Furthermore, the polymer gels formed in chlorinated solvents have been thoroughly characterized and studied, showing rheological properties comparable to those of polyacrylamide gels with a low crosslinker percentage. Given the thermal and chemical stability, the material was studied as a potential support for solid-state electrolytes. showing properties comparable to those of polyethylene glycol-based electrolytes, thus presenting great potential for the application of this new class of material in lithium-ion batteries.